5 Effective Ways to Breakdown Fungal Biofilms: A Comprehensive Guide
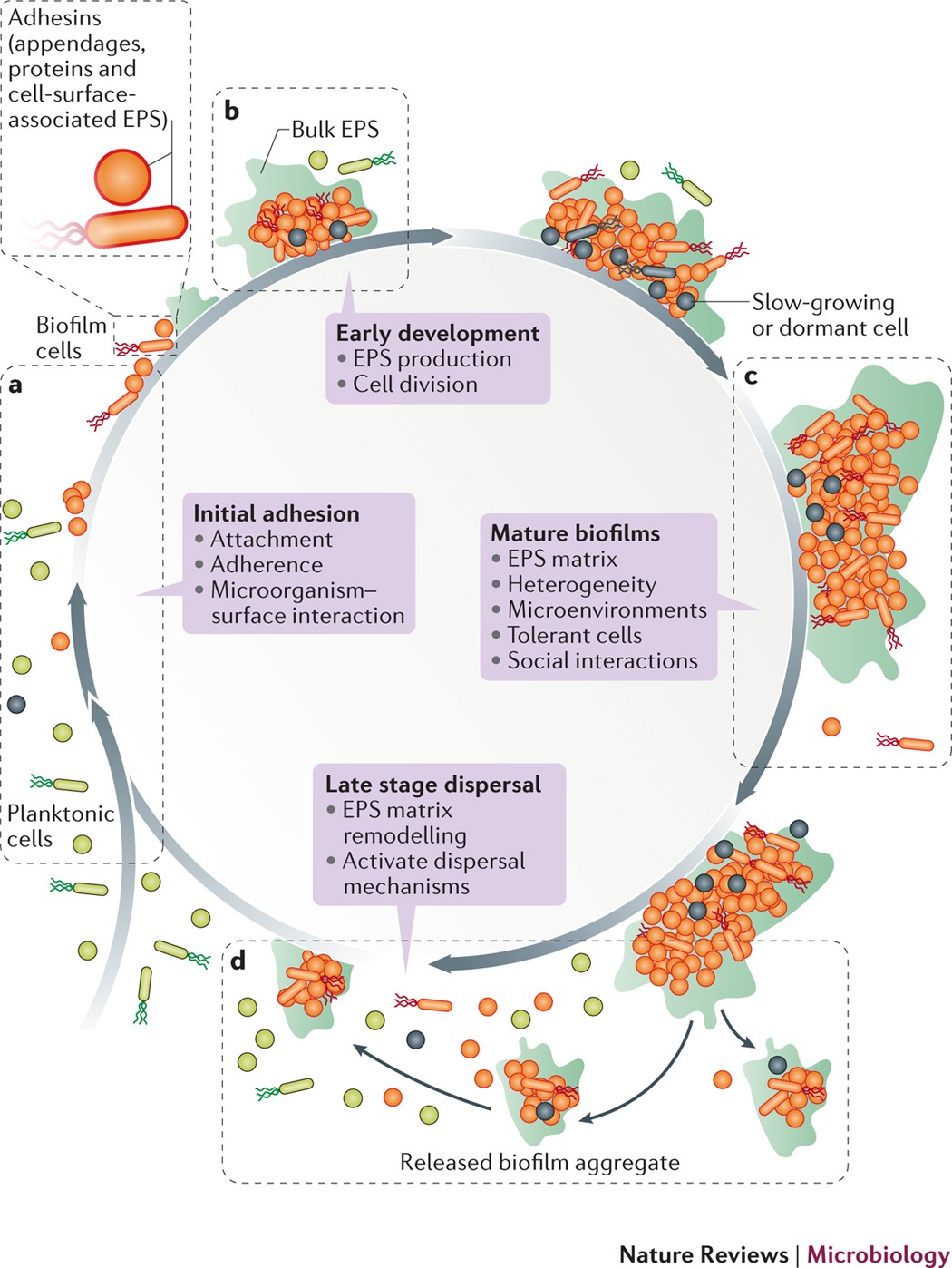
Fungal biofilms are persistent and resistant communities of microbes that can cause problematic infections. However, there are proven strategies to effectively breakdown these biofilms and improve treatment outcomes. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore five strategies that can help combat fungal biofilms and provide valuable insights for managing persistent fungal infections.
1. Antifungal Peptides: Incorporate antifungal peptides, such as defensins, cathelicidins, and histatins, into treatment regimens. These small protein molecules exhibit broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and can penetrate and destabilize fungal biofilms, enhancing the effectiveness of antifungal agents.
2. Use of Dispersal Agents: Disrupt the biofilm’s protective matrix by utilizing dispersal agents. D-amino acids, norspermidine, and cis-2-decenoic acid are effective in breaking down the extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) that hold biofilm cells together. This degradation allows better penetration of antifungal medications, increasing their efficacy.
3. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: Inhibit quorum sensing, a communication process that helps fungi establish and maintain biofilms. QS inhibitors such as farnesol and azithromycin impede the formation, maturation, and dispersal of fungal biofilms, enhancing treatment effectiveness. Ongoing research may lead to the development of more potent quorum sensing inhibitors in the future.
4. Combination Therapy: Synergistically use multiple antifungal agents in combination therapy. Combine echinocandins, azoles, and polyenes to reduce biofilm production and improve treatment efficacy. Combinations with QS inhibitors, dispersal agents, or peptides show enhanced antimicrobial effects, combating drug resistance and improving treatment outcomes.
5. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): Harness the power of photodynamic therapy to eradicate fungal cells and their biofilms. PDT utilizes a photosensitive compound, light, and oxygen to induce photochemical reactions. This therapy is effective in overcoming antifungal drug resistance, reducing inflammation, and promoting wound healing. Photosensitizers like methylene blue and 5-aminolevulinic acid show promise in eradicating or reducing Candida biofilms.
In conclusion, breaking down fungal biofilms is essential for successful treatment and infection control. By incorporating strategies such as antifungal peptides, dispersal agents, quorum sensing inhibitors, combination therapy, and photodynamic therapy, treatment outcomes can be significantly improved. Ongoing research aims to develop more effective methods to combat biofilms and enhance patient care in the management of persistent fungal infections.