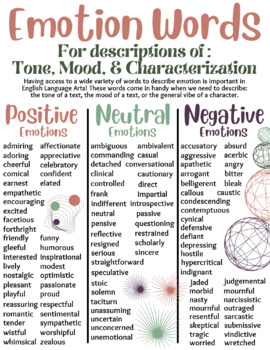
Exploring the Depths of Literary Criticism and Analysis
Literary criticism and analysis play a crucial role in understanding and appreciating works of literature. They enable readers to delve deeper into the layers of meaning, symbolism, and themes that authors embed in their writings. Whether you’re an avid reader, a student, or simply someone looking to enhance your understanding of literature, this blog post will take you on a journey through the depths of literary criticism and analysis. Join us as we explore key concepts, techniques, and approaches that will help you unlock the hidden treasures within books.
1. The Basics: Understanding Literary Criticism
Literary criticism is the evaluation, interpretation, and analysis of literary works. It involves examining various elements such as plot, characters, setting, themes, and literary devices used by the author. By studying these elements, critics aim to uncover the intended meaning and significance of a piece of literature. Familiarizing yourself with these basics will lay a solid foundation for further exploration.
2. Different Approaches to Literary Analysis
Literary analysis can be approached from various perspectives, each offering a unique lens through which to view a text. Some common approaches include:
– Formalist Criticism: This approach focuses on the formal elements of literature, such as language, structure, and style, to determine how they contribute to the overall meaning and effect of the work.
– Historical Criticism: Historical analysis examines the social, cultural, and historical context in which a piece of literature was written. By understanding the author’s background and the time period, readers can gain a deeper understanding of the work.
– Feminist Criticism: This approach explores the representation of gender roles, power dynamics, and women’s experiences within literature. It highlights the ways in which gender influences the interpretation and reception of texts.
– Psychological Criticism: Psychological analysis delves into the characters’ motivations, desires, and the subconscious elements of the text. It seeks to understand the psychological complexities and influences within a work.
– Postcolonial Criticism: This approach focuses on literature from formerly colonized regions, examining the effects of colonization, power dynamics, and cultural identity. It highlights the voices and experiences of marginalized groups.
3. Key Concepts in Literary Criticism
To deepen your analysis, it is essential to grasp key concepts commonly employed in literary criticism:
– Symbolism: Exploring symbols and their representations adds depth to understanding a work. Symbolism can be found in objects, characters, settings, or even abstract concepts that carry significant meaning.
– Themes: Identifying the central themes of a work provides insight into the underlying messages or moral lessons the author intends to convey.
– Motifs: Motifs are recurring elements, such as symbols, images, or themes, that contribute to the overall structure and meaning of a text.
– Allusion: Understanding allusions, references to other works, historical events, or cultural contexts, enhances comprehension and reveals the author’s intentions.
– Narrative Perspective: Examining the point of view, narrator reliability, and narrative structure sheds light on how the story is presented and affects the reader’s interpretation.
4. Tools for Literary Analysis
There are several tools and techniques that can aid in literary analysis:
– Close Reading: Close reading involves carefully examining specific passages, paying attention to details, word choices, and sentence structures. It allows for a deeper analysis of the author’s craft.
– Annotated Annotations: Keeping a record of your thoughts, questions, and observations while reading fosters a more engaged and critical approach. Create annotations in the margins, underline key passages, or use sticky notes to capture your insights.
– Comparative Analysis: Comparing and contrasting different works or authors encourages a broader perspective and highlights differences and similarities in style, themes, or techniques.
– Historical and Biographical Research: Conducting background research on the author’s life and the historical context in which the work was written provides valuable insights into the motivations and influences behind the text.
– Peer Discussions and Feedback: Engaging in conversations and seeking feedback from fellow readers or joining book clubs can offer diverse interpretations and enrich your understanding.
By utilizing these tools and techniques, you can embark on a fulfilling journey through the rich tapestry of literature, gaining a deeper appreciation for the craft and the meanings hidden within.
In conclusion, literary criticism and analysis provide a gateway to uncovering the depths of meaning and significance within literature. By understanding the basic concepts, exploring different approaches, and utilizing various tools, you can enhance your comprehension and appreciation of literary works. Embrace the adventure of literary analysis, and discover the treasures that lie within the pages of your favorite books. Happy exploring!